VO2 Max Test Toronto
What is Vo2 Max?
Your Vo2 Max reflects the maximal ability of muscles, lungs etc. to absorb, deliver and utilize oxygen during intensive exercise [1]. The greater your Vo2 Max, the better your endurance, and capacity to efficiently perform in competition and achieve desired fitness goals.
By completing a Vo2 Max Test, you’ll understand how well your body delivers oxygen-rich blood to working muscles and define target heart rate zones for optimal training response [1]. You can do the test using multiple modalities, usually performed on a treadmill or cycle. We recommend using one of these two devices because they provide more reliable readings in relation to cardiorespiratory research [1-3].
With the information gathered from Vo2 Max testing, our performance department can generate an optimized training regime built to enhance your oxygen efficiency for all aspects of movement and sport.
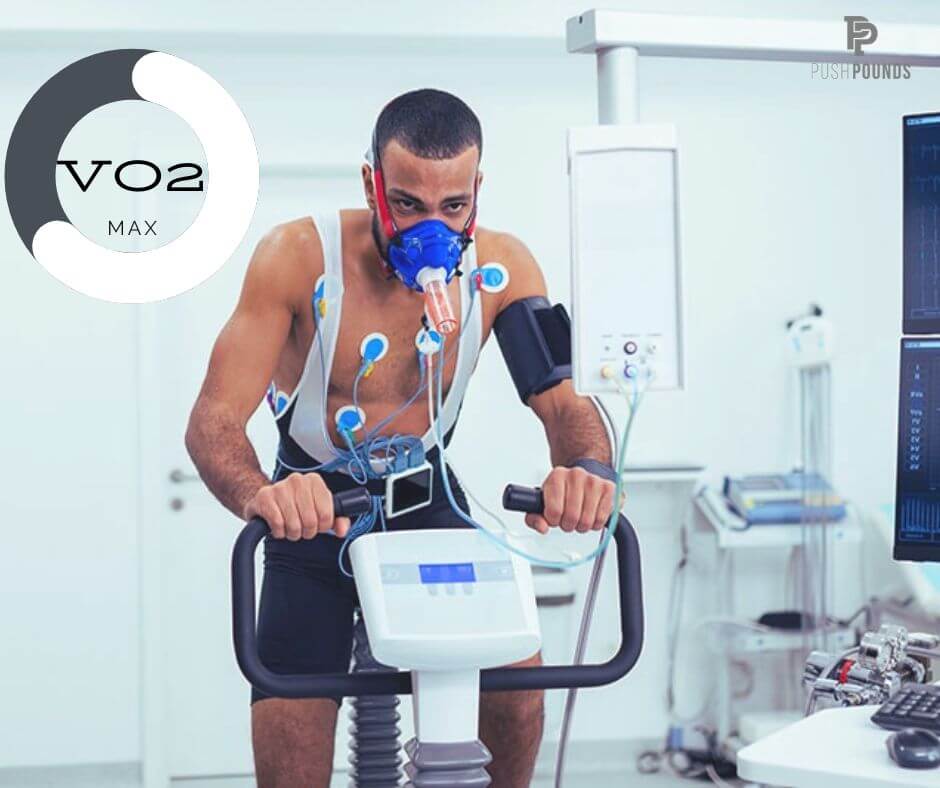
How is Vo2 Max Measured?
With a revolutionary VO2 system trusted by world leading researchers, we measure the oxygen content of the air you breathe in and out while running or cycling on a stationary bike. The difference between oxygen in and oxygen out is your oxygen consumption [2]. We progressively increase the intensity of the selected exercise until your oxygen consumption “levels off” or does not increase anymore. This is representing your Vo2 max. All these details and more are presented to you immediately following the test in an extensive report as seen below.
Why Take This Test?
The VO2 Max test, often referred to as the Gold Standard for endurance testing, is one of the most accurate assessments for current fitness level [1-2]. It is a direct measurement of oxygen consumption that gives the most precise indication possible.
To truly optimize performance, your training should be tailored specifically for your current level. This also ensuring no guess work is happening in any aspect of your programming.
What to Expect
Included in the Vo2 Max testing session is an information portion to understand all components of the testing protocol. We then will conduct a proper physical activation prior to the equipment fitting. Once the hardware is set, the test will begin with the selected modality. Following the test, a proper recovery session will occur followed by an in-depth breakdown of the test results, that the athlete/patient will take home with them.
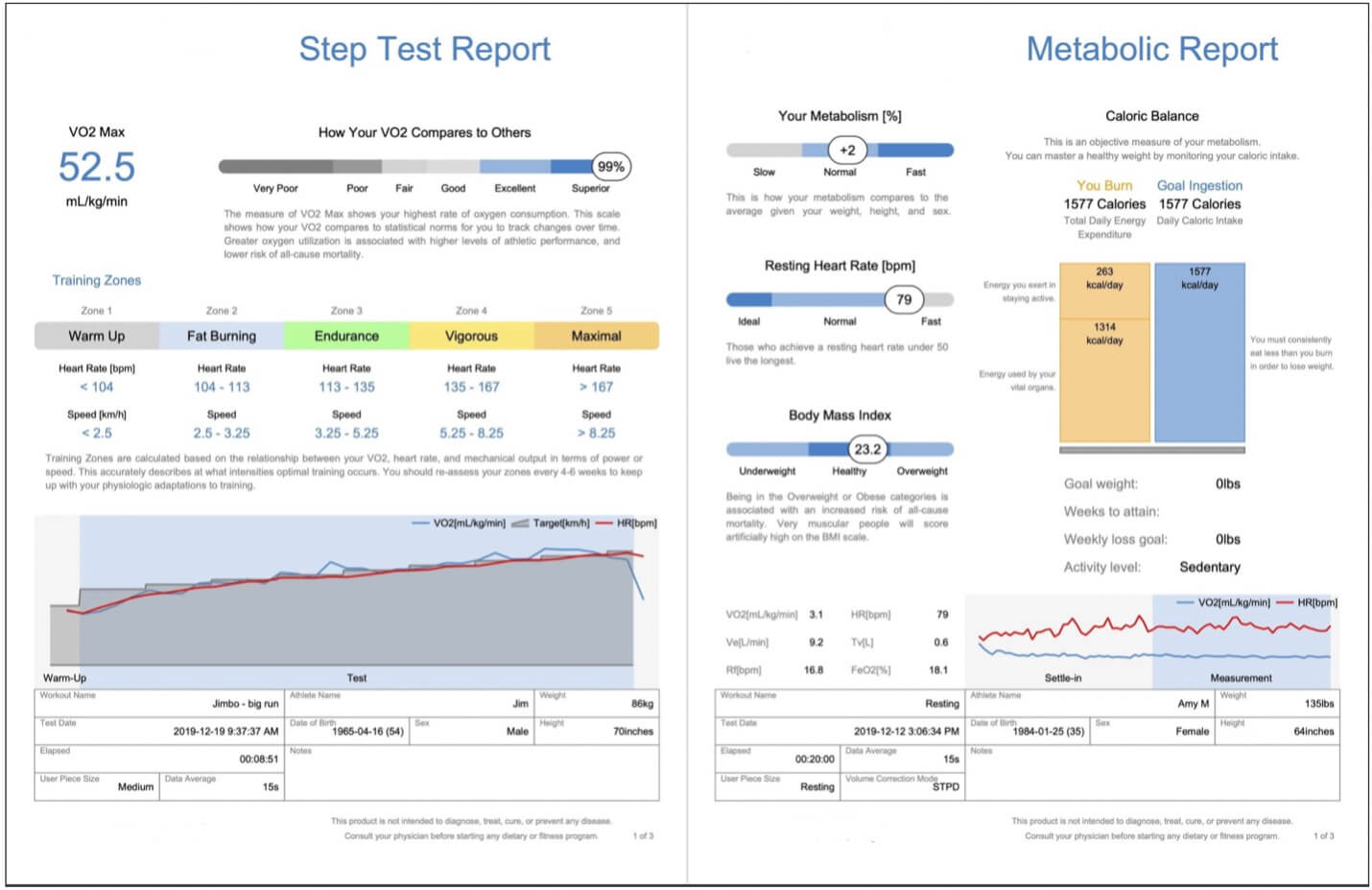
Identify Your Target Heart Rate Zones
Discover your body’s reaction to exercise and mark your heart rate zones according to it.
Understanding What Your Body Is Using For Fuel
As you increase the intensity of your workouts, carbohydrates (sugars) become a larger portion of your energy. See how different heart rates affect your fat and sugar-burning response.
Discover Your Rate of Calorie Burn During Exercise
To accurately track how many calories you burn during exercise, you need to know how many calories are burned per hour at different heart rates.
The Report
This 5-page report will show your VO2 Max Score, Anaerobic Threshold Heart Rate, Custom Training Heart Rate Zones and the number of calories burned at different intensities.

VO2 Max Test Сost
The VO2 Max Test is a valuable tool for runners and cyclists to measure their fitness. It can take up an hour of your time and cost $140, 2 scans are $260, but you’ll save money by purchasing the test package instead and getting more data!
Most people think they can just guess how fast to walk or run to achieve maximum fat loss, but this isn’t always the case.
Without knowing your VO2 Max, you could be wasting valuable time and energy by doing workouts that are too easy or too hard for you.
The VO2 Max Test is a valuable way to identify different zones of exertion and determine what type of workouts would be best suited based on their results.
VO2 Max Chart
What’s a good VO2 Max for my age and gender?
V02 Max scores can vary depending on several factors other than fitness, such as sex, age, and genetics, but the Vo2 Max measurement for the average person between the ages of 30 and 40 is likely to be around:
- Women – 31 ml of oxygen/kg body weight per minute
- Men – 42 ml oxygen/kg body weight per minute
This means: that the average woman (30-40 years old) consumes about 31 ml of oxygen for each kilogram of her weight during each minute of running. And the average man (30-40 years old) consumes 42 ml of oxygen for every kilogram of weight for every minute of running.
A physically fit person in the same age range is likely to have a Vo2 Max of about:
- Women – 45+ ml of oxygen/kg body weight per minute
- Men – 51+ ml oxygen/kg body weight per minute
The table below shows the average score for men and women of different ages.
VO2 Max Chart for Women (ml/kg/min)
| Classification | 18-20 | 21-35 | 36-45 | 46-55 | 56-65 | 66+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very Poor | <28 | <26 | <22 | <20 | <18 | <17 |
| Poor | 28-32 | 26-30 | 22-26 | 20-24 | 18-21 | 17-18 |
| Below average | 33-37 | 31-34 | 27-30 | 25-27 | 22-24 | 19-21 |
| Average | 38-41 | 35-38 | 31-33 | 28-30 | 25-27 | 22-24 |
| Above average | 42-46 | 39-44 | 34-37 | 21-33 | 28-31 | 25-27 |
| Good | 47-56 | 45-52 | 38-45 | 34-40 | 32-37 | 28-32 |
| Excellent | >56 | >52 | >45 | >40 | >37 | >32 |
VO2 Max Chart for Men (ml/kg/min)
| Classification | 18-25 | 26-35 | 36-45 | 46-55 | 56-65 | 66+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very poor | <30 | <30 | <26 | <25 | <22 | <20 |
| Poor | 30-36 | 30-34 | 26-30 | 25-28 | 22-25 | 20-21 |
| Below average | 37-41 | 35-39 | 31-34 | 29-31 | 26-29 | 22-25 |
| Average | 42-46 | 40-42 | 35-38 | 32-35 | 30-31 | 26-28 |
| Above average | 47-51 | 43-48 | 39-42 | 36-38 | 32-35 | 29-32 |
| Good | 52-60 | 49-56 | 43-51 | 39-45 | 36-41 | 33-37 |
| Excellent | >60 | >56 | >51 | >45 | >41 | >37 |
Can I improve my VO2 max?
You can get the most out of your Vo2 max by working at high intensity. Many running coaches recommend training with around 90 to 95 percent maximum heart rate, which helps strengthen muscles between beats and increase blood volume per beat for a strong foundation when it comes time to race-win or place well on top finishes!
What the price?
$140 plus tax
Our team
Dr. Honey Mzadeh, PhD, MSc, BSc (Hons) PHD – Cardiovascular Exercise Physiology
Contraindications per AHA Guidelines
Absolute Contraindications
- Unstable angina or recent myocardial infarction (within two days)
- Uncontrolled cardiac dysrhythmias associated with symptoms or hemodynamic compromise
- Symptomatic severe aortic stenosis or aortic dissection
- Uncontrolled heart failure
- Acute pulmonary embolus or infarction
- Acute myocarditis, pericarditis, or endocarditis
- Acute systemic infection accompanied with symptoms
Relative Contraindications
- Moderate valvular stenosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmias
- Left main coronary artery stenosis
- Severe pulmonary or untreated severe systemic arterial hypertension
- High degree AV block
References
- Lee and X. . Zhang, “Physiological determinants of VO2max and the methods to evaluate it: A critical review,” Science & sports, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 259–271, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2020.11.006.
- Bennett, G. Parfitt, K. Davison, and R. Eston, “Validity of Submaximal Step Tests to Estimate Maximal Oxygen Uptake in Healthy Adults,”Sports medicine (Auckland), vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 737–750, 2015, doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0445-1.
- Petot, R. Meilland, L. Le Moyec, L. Mille-Hamard, and V. L. Billat, “A new incremental test for VO2max accurate measurement by increasing VO2max plateau duration, allowing the investigation of its limiting factors,”European journal of applied physiology, vol. 112, no. 6, pp. 2267–2276, 2011, doi: 10.1007/s00421-011-2196-5.


